Install the Envoy proxy
Time to install the Envoy proxy. We will use AWS Systems Manager (SSM) to configure the EC2 instances that serve the frontend microservice. We will have to create an SSM document to define the actions that SSM will perform on the managed instances. Documents use JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) or YAML.
- Execute the following script in your Cloud9 environment to create the SSM document.
# Create YAML file #
cat <<-"EOF" > /tmp/install_envoy.yml
---
schemaVersion: '2.2'
description: Install Envoy Proxy
parameters:
region:
type: String
meshName:
type: String
vNodeName:
type: String
ignoredUID:
type: String
default: '1337'
proxyIngressPort:
type: String
default: '15000'
proxyEgressPort:
type: String
default: '15001'
appPorts:
type: String
egressIgnoredIPs:
type: String
default: '169.254.169.254,169.254.170.2'
egressIgnoredPorts:
type: String
default: '22'
mainSteps:
- action: aws:configureDocker
name: configureDocker
inputs:
action: Install
- action: aws:runShellScript
name: installEnvoy
inputs:
runCommand:
- |
#! /bin/bash -ex
sudo yum install -y jq
$(aws ecr get-login --no-include-email --region {{region}} --registry-ids 840364872350)
# Install and run envoy
sudo docker run --detach \
--env APPMESH_VIRTUAL_NODE_NAME=mesh/{{meshName}}/virtualNode/{{vNodeName}} \
--env ENABLE_ENVOY_XRAY_TRACING=1 \
--log-driver=awslogs \
--log-opt awslogs-region={{region}} \
--log-opt awslogs-create-group=true \
--log-opt awslogs-group=appmesh-workshop-frontend-envoy \
--log-opt tag=ec2/envoy/{{.FullID}} \
-u {{ignoredUID}} --network host \
840364872350.dkr.ecr.{{region}}.amazonaws.com/aws-appmesh-envoy:v1.11.2.0-prod
- action: aws:runShellScript
name: installXRay
inputs:
runCommand:
- |
#! /bin/bash -ex
XRAY_HOST=https://s3.dualstack.{{region}}.amazonaws.com
XRAY_PATH=aws-xray-assets.{{region}}/xray-daemon/aws-xray-daemon-3.x.rpm
# Install and run xray daemon
sudo curl $XRAY_HOST/$XRAY_PATH -o /tmp/xray.rpm
sudo yum install -y /tmp/xray.rpm
- action: aws:runShellScript
name: enableRouting
inputs:
runCommand:
- |
#! /bin/bash -ex
APPMESH_LOCAL_ROUTE_TABLE_ID="100"
APPMESH_PACKET_MARK="0x1e7700ce"
# Initialize chains
sudo iptables -t mangle -N APPMESH_INGRESS
sudo iptables -t nat -N APPMESH_INGRESS
sudo iptables -t nat -N APPMESH_EGRESS
sudo ip rule add fwmark "$APPMESH_PACKET_MARK" lookup $APPMESH_LOCAL_ROUTE_TABLE_ID
sudo ip route add local default dev lo table $APPMESH_LOCAL_ROUTE_TABLE_ID
# Enable egress routing
# Ignore egress redirect based UID, ports, and IPs
sudo iptables -t nat -A APPMESH_EGRESS \
-m owner --uid-owner {{ignoredUID}} \
-j RETURN
sudo iptables -t nat -A APPMESH_EGRESS \
-p tcp \
-m multiport --dports "{{egressIgnoredPorts}}" \
-j RETURN
sudo iptables -t nat -A APPMESH_EGRESS \
-p tcp \
-d "{{egressIgnoredIPs}}" \
-j RETURN
# Redirect everything that is not ignored
sudo iptables -t nat -A APPMESH_EGRESS \
-p tcp \
-j REDIRECT --to {{proxyEgressPort}}
# Apply APPMESH_EGRESS chain to non-local traffic
sudo iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT \
-p tcp \
-m addrtype ! --dst-type LOCAL \
-j APPMESH_EGRESS
# Enable ingress routing
# Route everything arriving at the application port to Envoy
sudo iptables -t nat -A APPMESH_INGRESS \
-p tcp \
-m multiport --dports "{{appPorts}}" \
-j REDIRECT --to-port "{{proxyIngressPort}}"
# Apply APPMESH_INGRESS chain to non-local traffic
sudo iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING \
-p tcp \
-m addrtype ! --src-type LOCAL \
-j APPMESH_INGRESS
EOF
# Create ssm document #
aws ssm create-document \
--name appmesh-workshop-installenvoy \
--document-format YAML \
--content file:///tmp/install_envoy.yml \
--document-type Command
- Create an association using State Manager. An association is a binding of the intent (described in the document) to a target specified by either a list of instance IDs or a tag query. Use the following command to create an association. Note that you are specifying a tag query in the target parameter and using the Frontend Auto Scaling group name.
# Define variables #
AUTOSCALING_GROUP=$(jq < cfn-output.json -r '.RubyAutoScalingGroupName'); \
# Create ssm association #
aws ssm create-association \
--name appmesh-workshop-installenvoy \
--association-name appmesh-workshop-state \
--targets "Key=tag:aws:autoscaling:groupName,Values=$AUTOSCALING_GROUP" \
--max-errors 0 \
--max-concurrency 50% \
--parameters \
"region=$AWS_REGION,
meshName=appmesh-workshop,
vNodeName=frontend,
appPorts=3000"
- Wait for association to complete.
# Check association status #
_list_association() {
aws ssm list-associations \
--association-filter key="AssociationName",value="appmesh-workshop-state" | \
jq -r ' .Associations[].Overview.Status'
}
until [ $(_list_association) != "Pending" ]; do
echo "Association is pending ..."
sleep 10s
if [ $(_list_association) == "Success" ]; then
echo "Association created"
break
fi
done
Similarly to what you did with the Crystal backend, validate Envoy is working appropiately on the EC2 instances. This time, instead of querying the application, you will query the Envoy server state endpoint.
- Start a Session Manager session with any of the EC2 instances.
AUTO_SCALING_GROUP=$(jq < cfn-output.json -r '.RubyAutoScalingGroupName');
TARGET_EC2=$(aws ec2 describe-instances \
--filters Name=tag:aws:autoscaling:groupName,Values=$AUTO_SCALING_GROUP | \
jq -r ' .Reservations | first | .Instances | first | .InstanceId')
aws ssm start-session --target $TARGET_EC2
- Curl the server state endpoint.
curl -v localhost:9901/server_info
You sould see an output like this:
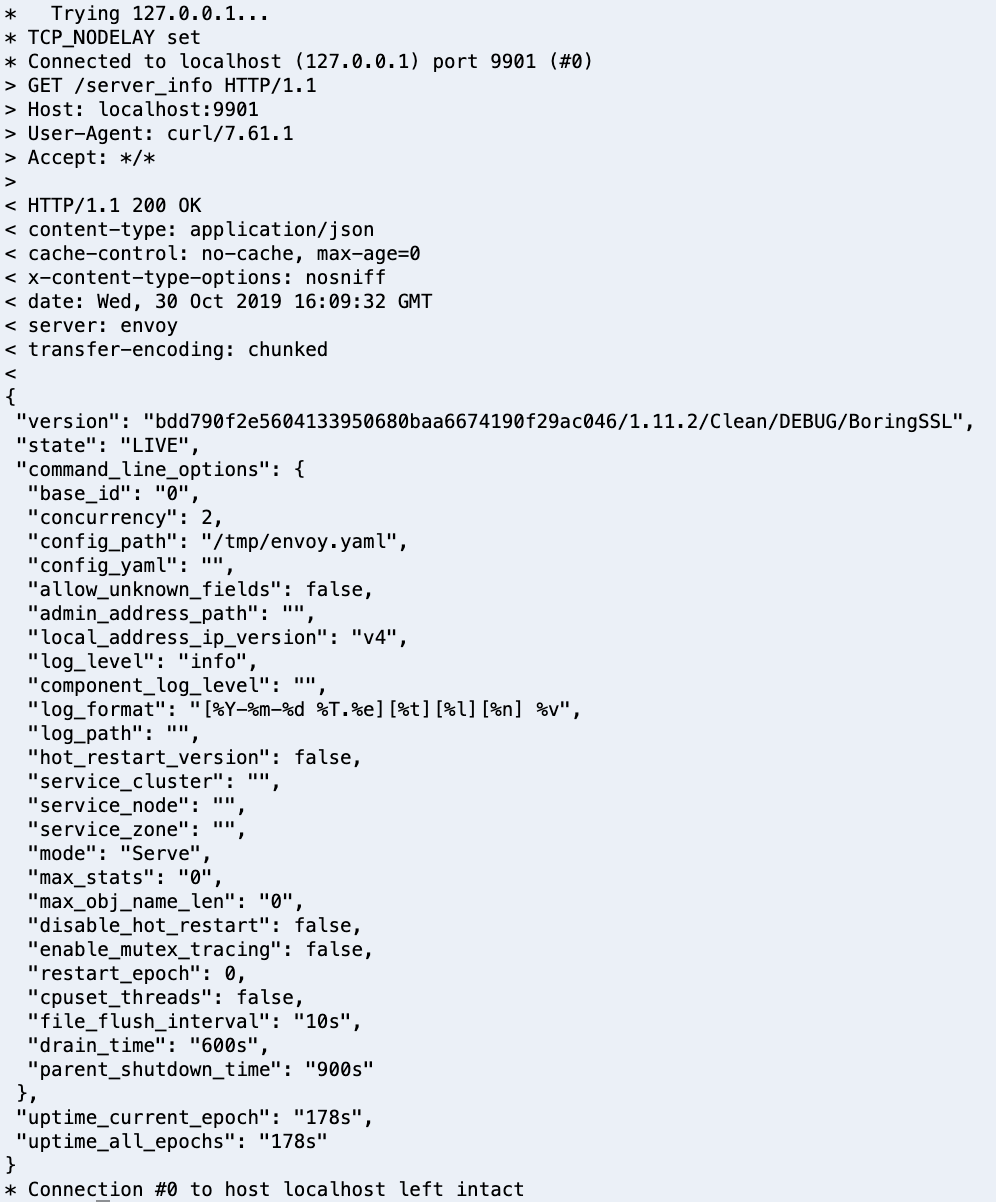
Notice the value of the state property. LIVE means the server is live and serving traffic.
- Compare the responses when connecting directly to the frontend app vs connecting to the loadbalancer in front of frontend service. To do so, run the following command from the ssm Session:
# run this inside ssm session
curl -v localhost:3000
You should see the following output:
* Rebuilt URL to: localhost:3000/
* Trying 127.0.0.1...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to localhost (127.0.0.1) port 3000 (#0)
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: localhost:3000
> User-Agent: curl/7.61.1
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
< X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
< X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
< Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
< ETag: W/"82e0fba05d3d87efbc72c560ae2a19d6"
< Cache-Control: max-age=0, private, must-revalidate
< X-Request-Id: 2e8aaa9c-f7a8-47fc-94d8-8baf33dd06c7
< X-Runtime: 0.018936
< Connection: close
< Server: thin
Now, exit from the ssm session and run the following commands from the Cloud9 environment:
# Exit the ssm session
exit
# Curl the Load Balancer URL
curl -v $(jq -r .ExternalLoadBalancerDNS cfn-output.json )
The output should be similar to this:
* Rebuilt URL to: ExtLB-appmesh-workshop-972091076.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com/
* Trying 52.37.89.182...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to ExtLB-appmesh-workshop-972091076.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com (52.37.89.182) port 80 (#0)
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: ExtLB-appmesh-workshop-972091076.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com
> User-Agent: curl/7.61.1
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Date: Mon, 18 Nov 2019 05:10:10 GMT
< Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
< Transfer-Encoding: chunked
< Connection: keep-alive
< x-frame-options: SAMEORIGIN
< x-xss-protection: 1; mode=block
< x-content-type-options: nosniff
< etag: W/"073fd9b223f3ff9ee0c4d911ed924d31"
< cache-control: max-age=0, private, must-revalidate
< x-request-id: 656fbfd1-e85c-9e1c-8069-78e04f7b8a19
< x-runtime: 0.013817
< server: envoy
< x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 14
Notice the change in server header. from thin to envoy when calling the URL from the external world.